5G pogosto uporabljena terminologija
AAS (Aktivni antenski sistem), aktivni antenski sistem, lahko vidimo kot kombinacijo RRU in antene, ki združuje aktivno radiofrekvenčno sprejemno-sprejemno enoto in pasivni antenski niz.

V preteklosti, RRU in antena sta bila ločena, in oba sta bila povezana prek radijskega frekvenčnega podajalnika. Po integraciji RF oddajne enote in antenskega niza, AAS lahko podpira tehnologijo Massive MIMO, kar lahko zmanjša izgubo RF podajalnika, povečati pokritost in zmogljivost omrežja, ter zmanjšati prostor in vzdrževalno obremenitev.
OF (Funkcija aplikacije), funkcijo aplikacije. AF je podoben aplikacijskemu strežniku, ki sodeluje z drugimi NF-ji nadzorne ravnine jedrnega omrežja 5G in zagotavlja poslovne storitve. AF lahko obstaja za različne storitve aplikacij, in je lahko v lasti operaterja ali zaupanja vredne tretje osebe.

AMF (Funkcija upravljanja dostopa in mobilnosti), funkcija upravljanja dostopa in mobilnosti. AMF je odgovoren za funkcije, kot je preverjanje identitete UE, avtentikacija, registracija, upravljanje mobilnosti, in upravljanje povezav. V primerjavi s 4G EPC, funkcija AMF je podobna funkciji MME.
IZVEDBA (Funkcija strežnika za preverjanje pristnosti), funkcijo strežnika za preverjanje pristnosti, je odgovoren za avtentikacijo in avtentikacijo.
Backhaul, backhaul, se nanaša na prenosno omrežje, ki povezuje radijsko dostopovno omrežje (RAN) in mobilno jedrno omrežje. Pod porazdeljenim RAN (D-RAN) arhitektura, backhaul povezuje bazno postajo z jedrnim omrežjem; pod centralizirano RAN (C-RAN) arhitektura, povezuje centralno razporejeno skupino BBU/DU v oblaku z osrednjim omrežjem.
BBU (Enota osnovnega pasu) se nanaša na enoto, odgovorno za obdelavo signalov osnovnega pasu v sistemu bazne postaje.
Oblikovanje snopa, oblikovanje žarka. Radijski valovi so kot valovi. Ko trčita (posegati) drug z drugim, postanejo močnejši ali šibkejši, odvisno kako trčijo. Oblikovanje snopa izkorišča to funkcijo. Oddaja isti signal skozi več antenskih enot, in prilagaja fazo in amplitudo vsake antenske enote, tako da se radijski valovi povečajo v določeni smeri, in se med seboj izničijo in oslabijo v drugih smereh. Naj bo širjenje brezžičnega signala bolj koncentrirano kot žarki, ki lahko poveča pokritost in zmanjša motnje.

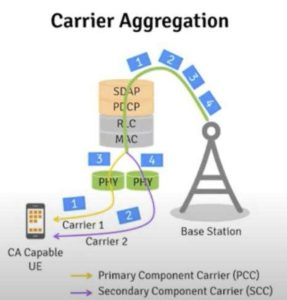
CA (Združevanje nosilcev), združevanje nosilcev, je združiti dva ali več nosilcev (kanalov) uporabnikom zagotoviti višjo hitrost prenosa podatkov. CA is like merging two or more roads together to make the road wider.
Control Plane, the control plane, is mainly responsible for processing non-data packet forwarding, including control signaling such as mobility management, connection establishment, and quality of service (QoS).
C-RAN (Centralized/Cloud-Radio Access Network), centralized/cloud-based radio access network), C stands for Centralized, Cloud, Clean and Cooperative, and refers to the centralized and cloud-based/virtualized deployment of CU and DU , Which can improve the coordinated scheduling between cells, achieve more flexible resource scheduling and load balancing, and reduce deployment and operation and maintenance costs.

CU (Centralized Unit), the central unit. 4G base station equipment is composed of BBU (baseband unit) and RRU (remote radio unit). RRU je običajno razširjen na mesto blizu antene. BBU in RRU sta povezana z optičnim vlaknom, in RRU in antena sta povezana s podajalnikom. Oprema bazne postaje 5G deli BBU na CU (Centralna enota) in TI (Porazdeljena enota), in je povezan z AAU (Enota aktivne antene) prek optičnih vlaken. CU je odgovoren za gostovanje RRC (Plast nadzora radijskih virov), SDAP (Protokol za prilagajanje podatkov storitve) in PDCP (Sloj protokola za konvergenco paketnih podatkov) podplasti bazne postaje 5G, ki centralno nadzoruje eno ali več enot DU.

SKODELICE (Razdelitev nadzorne in uporabniške ravnine), ločitev funkcij nadzorne in uporabniške ravnine, se nanaša na ločitev funkcij nadzorne ravnine, odgovornih za upravljanje povezave, Politike QoS, avtentikacija uporabnika in druge funkcije iz uporabniške ravnine funkcije, odgovorne za posredovanje podatkovnega prometa za poenostavitev in poenotenje Celotna omrežna arhitektura naredi jedrno omrežje bolj prilagodljivo in učinkovito. Pod arhitekturo CUPS, saj se število prometa povečuje, Funkcije uporabniške ravnine je mogoče neodvisno razširiti brez vpliva na nadzorno ravnino, primeren pa je tudi za centralizirano upravljanje nadzorne ravnine.

DN (Podatkovno omrežje) se nanaša na omrežje, ki zagotavlja storitve, osredotočene na podatke, kot je internet, storitve v oblaku/OTT, in podjetniška omrežja.

D-RAN (Distribuirano radijsko dostopovno omrežje), porazdeljeno radijsko dostopovno omrežje. V primerjavi z arhitekturo C-RAN, D-RAN is a traditional RAN architecture, which installs BBUs and RUs on distributed sites.
DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing), dynamic spectrum sharing, refers to 5G NR and 4G wireless sharing the same spectrum resources, and dynamic allocation of time-frequency resources to 4G and 5G users, usually by sharing the currently used 4G middle and low frequency bands to achieve 5G NR is introduced into the 4G coverage area, so that 5G wide coverage can be realized at low cost and quickly.

DU (Porazdeljena enota), a distributed unit, hosts the nodes of the RLC, MAC, and PHY sublayers of the 5G base station, and is mainly responsible for the MAC layer functions and some physical layer functions that deal with real-time requirements.
eCPRI (Enhanced Common Public Radio Interface), an enhanced common public radio interface, is a fronthaul interface protocol used to connect wireless base stations BBU/DU and AAU. Compared with CPRI in the 4G era, eCPRI’s data transmission method supports Ethernet technology, supports physical layer function splitting, extends the fronthaul bandwidth by 10 krat, and greatly improves the efficiency and flexibility of the fronthaul.

Edge Cloud refers to the deployment of cloud at the edge of the network to bring computing power and applications closer to users, which can greatly reduce network delay and backhaul burden, bring users a more extreme business experience, and promote more Many application innovations.

EPC (Evolved Packet Core), evolved packet core network, 4G LTE core network.
eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) je eden od treh scenarijev izboljšane mobilne širokopasovne povezave in 5G. To je prvi in najobsežnejši scenarij 5G. To pomeni, da lahko 5G zagotovi boljšo mobilno širokopasovno izkušnjo kot prejšnji standardi in tehnologije mobilne komunikacije. Najvišja hitrost in povprečna hitrost prenosa podatkov se povečata za več kot 10 krat.
en-gNB, gNB je bazna postaja 5G. V možnosti 3 način uvajanja, bazna postaja 5G je zasidrana na bazno postajo 4G in osrednje omrežje 4G EPC. V tem času, bazna postaja 5G se imenuje en-gNB.

Dvojna povezava med EN-DC, E-UTRA (LTE) in 5G NR pomeni, da je UE hkrati povezan z brezžičnima tehnologijama LTE in NR, in se nanaša tudi na možnost 3 način uvajanja.
FlexE (Prilagodljiv Ethernet), standard, ki ga je določil Forum za optično povezovanje (OIF) v 2016, introduces the FlexE Shim layer on the basis of standard Ethernet, and realizes the decoupling of the MAC and PHY layers. Realize flexible rate adaptation, expand network capacity by bundling multiple physical links to meet the large bandwidth requirements of 5G, and support multiple services through the Shim layer time slot configuration to achieve physical isolation between multiple services . For end-to-end 5G network slicing, FlexE is a key technology that can implement network hard slicing on the basis of shared network infrastructure and achieve business isolation.

FR1 (Frequency range 1), one of the two frequency ranges specified by 5G NR, FR1 refers to the sub-6GHz frequency band, covering the range between 410 MHz and 7125 MHz.
FR2 (Frequency range 2), one of the two frequency ranges specified by 5G NR, FR2 includes the millimeter wave frequency band between 24.25 GHz in 52.6 GHz. Fronthaul, fronthaul, se nanaša na prenosno omrežje, kjer se RU poveže z DU v arhitekturi C-RAN.
FWA (Fiksni brezžični dostop) se nanaša na zmogljivost velike pasovne širine, ki temelji na 5G NR, ki uporablja brezžični dostop 5G za zamenjavo zadnje milje optičnih vlaken do doma, s čimer se odpravi potreba po polaganju vlaken in zagotovi poceni in prilagodljiv širokopasovni dostop za podjetja in družinske storitve.
gNB (gNodeB), polno ime naslednje generacije vozlišča B, je poimenovanje baznih postaj 5G.
Trdo rezanje se nanaša na dodeljevanje omrežnih virov različnim strankam ali aplikacijam na popolnoma izoliran način, ki temelji na programski opremi 5G in arhitekturi oblaka (rezanje omrežja).
IMT-Advanced (Mednarodne mobilne telekomunikacije - napredne), nomenklatura 4G in 4,5G ITU, se nanaša na mobilne sisteme, ki presegajo zmogljivosti IMT-2000 (3G).
IMT-2020 (International Mobile Telecommunications-2020), the ITU’s 5G naming, aims to study IMT in 2020 and beyond.
Low Band, low frequency band, usually refers to the frequency band less than 1GHz. It is currently mainly used for 3G and 4G. It has the characteristics of long coverage distance and strong wall penetration capability. However, the low frequency band has a small bandwidth and a small data capacity that can be carried.
LTE (Long-Term Evolution), long-term evolution, refers to the 4G mobile communication standard. The network data rate of LTE is 10 times faster than that of 3G.
LTE-A (Long-Term Evolution-Advanced) refers to further enhancements to the LTE standard. In order to meet the requirements of IMT-Advanced, LTE-A was formally submitted to ITU-T at the end of 2009 and released as a 3GPP standard in 3GPP Release in 2011 10
Ogromen MIMO refers to the realization of three-dimensional precise beamforming and multi-stream multi-user multiplexing by integrating a large number of antenna units and more radio frequency channels on the base station side, thereby improving coverage and capacity, and reducing interference.

MEC (Multi-Access Edge Computing), refers to cloud computing at the edge of the network. It deploys computing power closer to users, which can reduce network latency and provide users with computing power and applications nearby. This can greatly enhance the business experience.
Mid-Band, the mid-band, usually refers to the frequency band between 1GHz and 6GHz. It is located between the low frequency band and the millimeter wave frequency band. It has both coverage and bandwidth capabilities and is regarded as a key frequency band for 5G.
Midhaul, midhaul, refers to the transmission network between CU and DU.
MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) refers to increasing the data transmission rate by using multiple antennas to simultaneously send and receive multiple data streams on the same channel.
mmWave, millimeter wave, a high frequency band between microwave and infrared, can provide large-capacity, high-speed 5G services, but the coverage and wall penetration capabilities are weak.
MTC (Machine Type Communications), machine type communication, refers to the communication between machines (things).
mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communications), one of the three major 5G application scenarios, refers to large-scale machines (things) in a characteristic area that communicate through application servers that reside on the core network.
MU-MIMO (Multiple user, multiple-input / multiple-output), multi-user MIMO, refers to the simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams spatially multiplexed to multiple users, which can double the capacity of the cell.
NEF (Network Exposure Function), a network opening function, is a network functional entity responsible for opening 5G core network capabilities to third parties or non-3GPP environments. You can treat it as a proxy, conversion point, or API aggregation point. Na primer, in edge applications, MEC (OF) needs to request PCF to offload traffic to the local server through NEF.
Network Slicing, rezanje omrežja, refers to the SLA requirements for network bandwidth, delay, varnost, zanesljivost, geographic coverage, itd., from the end-to-end network infrastructure on-demand to “slicing” multiple interactions from the end-to-end network infrastructure according to different industry customers or applications. Izolirano, varen, and SLA-guaranteed logical network.

NGC (Next Generation Core), the next generation core network, refers to the 5G core network.
ng-eNB, similar to en-gNB, in option 7, option 5, and option 4 načini, eNB (4G base station) connects to the 5G core network through the NG interface, which is called ng-eNB.
št (New Radio), New Radio, refers to the 3GPP 5G wireless system.
NRF (Network repository function), network repository function, is responsible for network function service registration, status monitoring, itd., realizes automatic management, selection and scalability of network function services, and allows each network function to discover the services provided by other network functions.
NSA (5G Non-Standalone Architecture), non-independent networking, refers to the use of dual connectivity, anchoring the 5G NR control plane to 4G LTE, and using the old 4G core network EPC. NSA is the early deployment architecture of 5G, which aims to use the existing 4G infrastructure to rapidly expand the 5G network.

NSSF (Network slice selection function), network slice selection function, manages network slice related information, na primer, is responsible for selecting network slices for the terminal and determining which AMF to use.
PCF (Policy Control Function), policy control function, is responsible for the 5G core network control plane function of policy control. Simply put, it mainly manages the QoS of each service data flow in the 5G core network.
P-GW (Packet Data Network Gateway), a packet gateway, is responsible for managing the QoS and bandwidth parameters in the LTE network, and acts as an IP router to connect the 4G core network to the external Internet. This function is replaced by UPF in the 5G core network.
Private 5G, 5G private network, refers to the enterprise or industry wireless private network constructed using the 3GPP 5G standard. The 3GPP standard defines two 5G private network deployment modes: SNPN (independent non-public network) and PNI-NPN (public network integrated NPN). PNI-NPN is what we often say “private public network”, which means that enterprises can share RAN with operators’ 5G public network, or share RAN and core network control plane, or share 5G public network end-to-end (end-to-end network 5G private network is deployed in a slicing method; SNPN is what we often call the “independent deployment mode”, which refers to the independent deployment of the entire 5G network from the base station to the core network to the cloud platform, which can be isolated from the operator’s 5G public network.

QoE (Quality of experience), the quality of experience, measures the overall satisfaction of customers with the network.
QoS (Quality of service), the quality of service, measures network capabilities such as delay, stopnja bitnih napak, and uptime.
RAN (Radio Access Network), wireless access network.
RU (Radio Unit), a wireless unit, is responsible for converting the digital signal from the DU into a radio frequency signal and transmitting it to the antenna, and converting the radio frequency signal from the antenna into a digital signal and transmitting it to the DU.
na (5G Standalone Architecture), 5G independent networking architecture, refers to 5G NR directly connected to the 5G core network (NG Core), no longer dependent on 4G, is a complete and independent 5G network

SBA (Service-based architecture), service-based architecture. The 5GC control plane introduces a service-based architecture (SBA). In SBA, each NF is not a one-to-one (point-to-point) povezava, but all NFs use the same protocol (HTTP/2) and share a communication channel. Each NF can communicate with any NF, and the connection between NFs It is more flexible and greatly enhanced flexible scalability.
SMF (Session management function), session management function, is responsible for establishing and managing sessions, UE IP address allocation and management, itd.
Small Cell, small cell, micro cell, refers to a cellular wireless access point that works in a low-power mode, and usually provides services for a small number of users in a small area. It can work in licensed or unlicensed spectrum.
SR (Segment Routing), segment routing, is a source routing technology that forwards data packets according to a dynamically defined path at the source node. SR supports two data forwarding planes, MPLS and IPv6.
S-GW (Serving Gateway), serving gateway, is mainly responsible for data packet transmission between eNB and P-GW. In the 5G core network, S-GW is replaced by UPF.
Soft Slicing, soft slicing, refers to the dynamic allocation of network resources for different services based on QoS technology.
TSN (Time Sensitive Networking), time sensitive network. Tradicionalna tehnologija Ethernet lahko doseže le “najboljši napor” komunikacije, in ne more izpolniti zahtev glede visoke zanesljivosti in nizke zakasnitve industrijskih proizvodnih aplikacij. Za industrijsko avtomatizacijo, je treba nadgraditi tradicionalno “najboljši napor” Ethernet zagotoviti “determinizem” “storitve. Ob istem času, obstaja veliko obstoječih industrijskih protokolov, ki so ločeni drug od drugega, in različni protokoli uporabljajo različne “jezik”, kar poveča težave pri integraciji ter stroške delovanja in vzdrževanja. V tem ozadju je nastal TSN. Opredeljen je s standardi IEEE, ki lahko zagotavlja deterministične storitve na osnovi standardne tehnologije Ethernet in zagotavlja standardizirane, enotne in ekonomične rešitve. Sistem 5G je integriran z omrežjem TSN. Temelji na zmožnostih nizke zakasnitve in visoke zanesljivosti 5G uRLLC, it can meet the four stringent functional requirements of the TSN architecture: time synchronization, low-latency transmission, high reliability and resource management, so as to satisfy the factory Industrial Internet use cases such as automation and power grid distribution automation.
UDM (Unified Data Management), unified data management, where all user data, network service configuration files, network access policies and other information are stored. Na primer, when a user initially connects to the network, the user information is verified through the data in UDM.
URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications), ultra-reliable and ultra-low-latency communications, one of the three major scenarios of 5G, aims to support services that are highly sensitive to delay and stability, and can be guaranteed by network slicing technology.
UPF (User Plane Function), the user plane function, is responsible for forwarding traffic between the wireless access network and Internet/DN, reporting traffic usage, QoS policy implementation, itd., corresponding to the user plane of S/PGW in 4G EPC.
V2X (Vehicle-to-everything), the Internet of Vehicles, aims to connect cars to the Internet, and to connect cars to cars, cars to people, cars and road infrastructure to realize the exchange of information between cars and the outside world, including Connectivity between V2N (vehicle and network/cloud), V2V (vehicle and vehicle), V2I (vehicle and road infrastructure), and V2P (vehicle and pedestrian).