5G često korištena terminologija
AAS (Aktivni antenski sustav), aktivni antenski sustav, može se promatrati kao kombinacija RRU i antene, koja integrira aktivnu radio -frekvencijsku primopredajnu jedinicu i pasivnu antenu.

U prošlosti, RRU i antena su razdvojeni, a njih dvoje su povezani putem radiofrekvencijskog ulagača. Nakon integriranja RF primopredajne jedinice i antene, AAS može podržati masivnu MIMO tehnologiju, što može smanjiti gubitak dovodnika RF, Povećajte pokrivenost i kapacitet mreže, i smanjiti radno opterećenje nebeskog prostora i održavanje.
OD (Funkcija aplikacije), Funkcija aplikacije. AF je sličan aplikacijskom poslužitelju, koji komunicira s ostalim 5G osnovnim mrežnim upravljačkim ravninama NFS i pruža poslovne usluge. AF može postojati za različite usluge aplikacija, i može biti u vlasništvu operatera ili pouzdane treće strane.

Amf (Funkcija pristupa i upravljanja mobilnošću), Funkcija pristupa i upravljanja mobilnošću. AMF je odgovoran za funkcije poput provjere identiteta UE, autentifikacija, prijava, upravljanje mobilnošću, i upravljanje vezama. U usporedbi s 4G EPC, Funkcija AMF -a je slična onoj MME.
Van (Funkcija poslužitelja za provjeru autentičnosti), funkcija poslužitelja za provjeru autentičnosti, odgovoran je za provjeru autentičnosti i provjere autentičnosti.
Povratak, backhaul, Odnosi se na prijenosnu mrežu koja povezuje mrežu Radio Access Network (Trčanje) i mobilna jezgranica. Pod distribuiranim ranom (D -ran) arhitektura, Backhaul povezuje baznu stanicu s osnovnom mrežom; Pod centraliziranim ranom (C -ran) arhitektura, povezuje centralno raspoređeni oblak bbu/du bazen na osnovnu mrežu.
BBU (Podloška) refers to the unit responsible for processing baseband signals in the base station system.
Beamforming, beam forming. Radio waves are like waves. When they collide (interfere) with each other, they become stronger or weaker, depending on how they collide. Beamforming takes advantage of this feature. It transmits the same signal through multiple antenna units, and adjusts the phase and amplitude of each antenna unit, so that radio waves are enhanced in a specific direction, and they cancel each other out and weaken in other directions. Make wireless signal propagation more concentrated like beams, which can increase coverage and reduce interference.

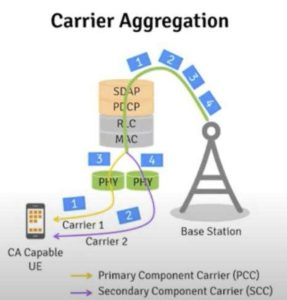
CA (Carrier Aggregation), carrier aggregation, is to aggregate two or more carriers (kanali) to provide users with a higher data rate. CA je poput spajanja dva ili više cesta kako bi cesta učinila širom.
Upravljačka ravnina, upravljačka ravnina, je uglavnom odgovoran za obradu prosljeđivanja paketa ne-podataka, uključujući kontrolnu signalizaciju poput upravljanja mobilnošću, uspostavljanje veze, i kvaliteta usluge (QoS).
C -ran (Centralizirana/oblačna pristupna mreža), Centralizirana/oblačna radio pristupna mreža), C označava centraliziranu, Oblak, Čist i kooperativan, i odnosi se na centralizirano i oblačno/virtualizirano raspoređivanje CU i DU , Koji mogu poboljšati koordinirani raspored između stanica, postići fleksibilnije raspoređivanje resursa i balansiranje opterećenja, i smanjiti troškove rada i rada i održavanja.

Pokrajina (Centralizirana jedinica), središnja jedinica. 4G Oprema bazne stanice sastoji se od BBU -a (podloška) i RRU (Daljinska radio jedinica). RRU se obično proširuje na mjesto blizu antene. BBU i RRU povezani su optičkim vlaknima, a RRU i antena povezani su hranilicom. Oprema bazne stanice 5G dijeli BBU na Cu (Središnja jedinica) I ti (Distribuirana jedinica), i povezan je s AAU -om (Aktivna antena) Kroz optička vlakna. CU je odgovoran za hosting RRC -a (Sloj upravljanja radio resursima), SDAP (Protokol prilagodbe podataka) i PDCP (Sloj protokola za konvergenciju paketa) Sublajci osnovne stanice 5G, koja centralno kontrolira jednu ili više DU jedinica.

Šalice (Kontrola i korisnička ravnina podijeljena), razdvajanje funkcije upravljačke ravnine i korisničke ravnine, odnosi se na odvajanje funkcija upravljačke ravnine odgovorne za upravljanje povezivanjem, Politike QOS -a, user authentication and other functions from the user plane functions responsible for data traffic forwarding to simplify and unify The entire network architecture makes the core network more flexible and efficient. Under the CUPS architecture, as the number of traffic increases, user plane functions can be independently expanded without affecting the control plane, and it is also convenient for centralized management of the control plane.

DN (Data Network) refers to a network that provides data-centric services such as the Internet, cloud/OTT services, and enterprise networks.

D -ran (Distributed Radio Access Network), a distributed radio access network. Compared with the C-RAN architecture, D-RAN is a traditional RAN architecture, which installs BBUs and RUs on distributed sites.
DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing), dynamic spectrum sharing, refers to 5G NR and 4G wireless sharing the same spectrum resources, and dynamic allocation of time-frequency resources to 4G and 5G users, usually by sharing the currently used 4G middle and low frequency bands to achieve 5G NR is introduced into the 4G coverage area, so that 5G wide coverage can be realized at low cost and quickly.

DU (Distribuirana jedinica), a distributed unit, hosts the nodes of the RLC, MAC, and PHY sublayers of the 5G base station, and is mainly responsible for the MAC layer functions and some physical layer functions that deal with real-time requirements.
eCPRI (Enhanced Common Public Radio Interface), an enhanced common public radio interface, is a fronthaul interface protocol used to connect wireless base stations BBU/DU and AAU. Compared with CPRI in the 4G era, eCPRI’s data transmission method supports Ethernet technology, supports physical layer function splitting, extends the fronthaul bandwidth by 10 times, and greatly improves the efficiency and flexibility of the fronthaul.

Edge Cloud refers to the deployment of cloud at the edge of the network to bring computing power and applications closer to users, which can greatly reduce network delay and backhaul burden, bring users a more extreme business experience, and promote more Many application innovations.

EPC (Evolved Packet Core), evolved packet core network, 4G LTE core network.
eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) jedan je od tri scenarija poboljšane mobilne širokopojasne mreže i 5G. To je prvi i najopsežniji scenarij 5G. To znači da 5G može pružiti bolje iskustvo mobilne širokopojasne mreže od prethodnih mobilnih komunikacijskih standarda i tehnologija. Vrhunska stopa i prosječna stopa podataka povećavaju se za više od 10 times.
En-gmb, GNB je 5G bazna stanica. U opciji 3 Način raspoređivanja, 5G bazna stanica usidrena je na 4G baznu stanicu i EPC 4G Core Network. U ovo vrijeme, 5G bazna stanica naziva se en-gnb.

Dvostruka veza između En-dc, E -Utra (LTE) i 5 g nr znači da je UE istovremeno spojeno i na LTE i NR bežične tehnologije, a također se odnosi na opciju 3 Način raspoređivanja.
Savijanje (Fleksibilan Ethernet), Standard definiran forumom za optičku povezanost (Oif) u 2016, introduces the FlexE Shim layer on the basis of standard Ethernet, and realizes the decoupling of the MAC and PHY layers. Realize flexible rate adaptation, expand network capacity by bundling multiple physical links to meet the large bandwidth requirements of 5G, and support multiple services through the Shim layer time slot configuration to achieve physical isolation between multiple services . For end-to-end 5G network slicing, FlexE is a key technology that can implement network hard slicing on the basis of shared network infrastructure and achieve business isolation.

FR1 (Frequency range 1), one of the two frequency ranges specified by 5G NR, FR1 refers to the sub-6GHz frequency band, covering the range between 410 MHz and 7125 MHz.
FR2 (Frequency range 2), one of the two frequency ranges specified by 5G NR, FR2 includes the millimeter wave frequency band between 24.25 GHz i 52.6 GHz. Fronthaul, fronthaul, odnosi se na prijenosnu mrežu u kojoj se ru povezuje na DU u C-Ran arhitekturi.
FWA (Fiksni bežični pristup) odnosi se na veliku mogućnost širine pojasa na temelju 5G NR, koji koristi 5G bežični pristup za zamjenu posljednjeg kilometra vlakana do kuće, čime se eliminira potreba za postavljanjem vlakana i pružanjem jeftinih i fleksibilnih širokopojasnih pristupa za poduzeća i obitelji usluga.
GNB (gnodeb), Puno ime čvora nove generacije b, je imenovanje 5G baznih stanica.
Teško rezanje odnosi se na raspodjelu mrežnih resursa različitim kupcima ili aplikacijama na potpuno izoliran način na temelju 5G softvera i arhitekture oblaka (mrežno rezanje).
Namijenjen (Međunarodne mobilne telekomunikacije-napredne), ITU nomenklatura 4G i 4,5 g, refers to mobile systems that exceed the capabilities of IMT-2000 (3G).
IMT-2020 (International Mobile Telecommunications-2020), the ITU’s 5G naming, aims to study IMT in 2020 and beyond.
Low Band, low frequency band, usually refers to the frequency band less than 1GHz. It is currently mainly used for 3G and 4G. It has the characteristics of long coverage distance and strong wall penetration capability. Međutim, the low frequency band has a small bandwidth and a small data capacity that can be carried.
LTE (Long-Term Evolution), long-term evolution, refers to the 4G mobile communication standard. The network data rate of LTE is 10 times faster than that of 3G.
LTE-A (Long-Term Evolution-Advanced) refers to further enhancements to the LTE standard. In order to meet the requirements of IMT-Advanced, LTE-A was formally submitted to ITU-T at the end of 2009 and released as a 3GPP standard in 3GPP Release in 2011 10
Massive MIMO refers to the realization of three-dimensional precise beamforming and multi-stream multi-user multiplexing by integrating a large number of antenna units and more radio frequency channels on the base station side, thereby improving coverage and capacity, and reducing interference.

MEC (Multi-Access Edge Computing), refers to cloud computing at the edge of the network. It deploys computing power closer to users, which can reduce network latency and provide users with computing power and applications nearby. This can greatly enhance the business experience.
Mid-Band, the mid-band, usually refers to the frequency band between 1GHz and 6GHz. It is located between the low frequency band and the millimeter wave frequency band. It has both coverage and bandwidth capabilities and is regarded as a key frequency band for 5G.
Midhaul, midhaul, refers to the transmission network between CU and DU.
MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) refers to increasing the data transmission rate by using multiple antennas to simultaneously send and receive multiple data streams on the same channel.
mmvalni, millimeter wave, a high frequency band between microwave and infrared, can provide large-capacity, high-speed 5G services, but the coverage and wall penetration capabilities are weak.
MTC (Machine Type Communications), machine type communication, refers to the communication between machines (things).
mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communications), one of the three major 5G application scenarios, refers to large-scale machines (things) in a characteristic area that communicate through application servers that reside on the core network.
MU-MIMO (Multiple user, multiple-input / multiple-output), multi-user MIMO, refers to the simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams spatially multiplexed to multiple users, which can double the capacity of the cell.
NEF (Network Exposure Function), a network opening function, is a network functional entity responsible for opening 5G core network capabilities to third parties or non-3GPP environments. You can treat it as a proxy, conversion point, or API aggregation point. Na primjer, in edge applications, MEC (OD) needs to request PCF to offload traffic to the local server through NEF.
Network Slicing, mrežno rezanje, refers to the SLA requirements for network bandwidth, delay, sigurnosti, pouzdanost, geographic coverage, itd., from the end-to-end network infrastructure on-demand to “slicing” multiple interactions from the end-to-end network infrastructure according to different industry customers or applications. Isolated, siguran, and SLA-guaranteed logical network.

NGC (Next Generation Core), the next generation core network, refers to the 5G core network.
ng-eNB, similar to en-gNB, in option 7, option 5, and option 4 modes, eNB (4G base station) connects to the 5G core network through the NG interface, which is called ng-eNB.
NR (New Radio), New Radio, refers to the 3GPP 5G wireless system.
NRF (Network repository function), network repository function, is responsible for network function service registration, status monitoring, itd., realizes automatic management, selection and scalability of network function services, and allows each network function to discover the services provided by other network functions.
NSA (5G Non-Standalone Architecture), non-independent networking, refers to the use of dual connectivity, anchoring the 5G NR control plane to 4G LTE, and using the old 4G core network EPC. NSA is the early deployment architecture of 5G, which aims to use the existing 4G infrastructure to rapidly expand the 5G network.

NSSF (Network slice selection function), network slice selection function, manages network slice related information, for example, is responsible for selecting network slices for the terminal and determining which AMF to use.
PCF (Policy Control Function), policy control function, is responsible for the 5G core network control plane function of policy control. Jednostavno rečeno, Uglavnom upravlja QoS -om svakog protoka podataka u 5G jezgrijskoj mreži.
P-GW (Gateway mreže paketa podataka), Gateway Packet, odgovoran je za upravljanje parametrima QOS i propusnosti u LTE mreži, i djeluje kao IP usmjerivač za povezivanje 4G Core mreže s vanjskim internetom. Ova je funkcija zamijenjena UPF -om u 5G Core Network.
Privatni 5G, 5G Privatna mreža, odnosi se na bežičnu privatnu mrežu poduzeća ili industrije izgrađenu pomoću standarda 3GPP 5G. Standard 3GPP definira dva načina implementacije privatne mreže 5G: SNPN (neovisna nejavna mreža) i PNI-NPN (Javna mreža integrirana NPN). Pni-npn je ono što često kažemo “privatna javna mreža”, što znači da poduzeća mogu dijeliti s operatorima’ 5G javna mreža, ili podijeliti upravljačku ravninu RAN i Core Network, or share 5G public network end-to-end (end-to-end network 5G private network is deployed in a slicing method; SNPN is what we often call the “independent deployment mode”, which refers to the independent deployment of the entire 5G network from the base station to the core network to the cloud platform, which can be isolated from the operator’s 5G public network.

QoE (Quality of experience), the quality of experience, measures the overall satisfaction of customers with the network.
QoS (Quality of service), the quality of service, measures network capabilities such as delay, stopa pogreške bitova, and uptime.
Trčanje (Radio Access Network), wireless access network.
RU (Radio Unit), a wireless unit, is responsible for converting the digital signal from the DU into a radio frequency signal and transmitting it to the antenna, and converting the radio frequency signal from the antenna into a digital signal and transmitting it to the DU.
na (5G Standalone Architecture), 5G independent networking architecture, refers to 5G NR directly connected to the 5G core network (NG Core), no longer dependent on 4G, is a complete and independent 5G network

SBA (Service-based architecture), service-based architecture. The 5GC control plane introduces a service-based architecture (SBA). In SBA, each NF is not a one-to-one (point-to-point) veza, but all NFs use the same protocol (HTTP/2) and share a communication channel. Each NF can communicate with any NF, and the connection between NFs It is more flexible and greatly enhanced flexible scalability.
SMF (Session management function), session management function, is responsible for establishing and managing sessions, UE IP adresa Raspodjela i upravljanje, itd.
Mala ćelija, mala ćelija, mikro stanica, odnosi se na staničnu bežičnu pristupnu točku koja djeluje u načinu male snage, i obično pruža usluge za mali broj korisnika u malom području. Može raditi u licenciranom ili nelicenciranom spektru.
SR (Usmjeravanje segmenta), usmjeravanje segmenta, je tehnologija usmjeravanja izvora koja prosljeđuje pakete podataka prema dinamički definiranom stazi na izvornom čvoru. SR podržava dvije ravnine za prosljeđivanje podataka, MPLS i IPv6.
S-GW (Kapija za posluživanje), kapija za posluživanje, uglavnom je odgovoran za prijenos paketa podataka između ENB i P-GW. U 5G osnovnoj mreži, S-GW je zamijenjen UPF-om.
Meko rezanje, meko rezanje, odnosi se na dinamičnu raspodjelu mrežnih resursa za različite usluge na temelju QoS tehnologije.
TSN (Vremenski osjetljivo umrežavanje), Mreža osjetljiva na vrijeme. Traditional Ethernet technology can only achieve “best effort” komunikacija, and cannot meet the high reliability and low latency requirements of industrial manufacturing applications. For industrial automation, it is necessary to upgrade the traditional “best effort” Ethernet to provide “determinism” “service. U isto vrijeme, there are many existing industrial protocols that are isolated from each other, and various protocols use different “Jezik”, which increases the difficulty of integration and the cost of operation and maintenance. It is under this background that TSN came into being. It is defined by IEEE standards, which can provide deterministic services based on standard Ethernet technology and provide standardized, unified and economical solutions. The 5G system is integrated with the TSN network. Based on the low-latency and high-reliability capabilities of 5G uRLLC, Može udovoljiti četiri stroga funkcionalna zahtjeva TSN arhitekture: vremenska sinkronizacija, prijenos niske karata, Visoka pouzdanost i upravljanje resursima, kako bi se zadovoljile slučajeve upotrebe industrijskog interneta kao što su automatizacija i automatizacija distribucije električne mreže.
Udm (Ujedinjeno upravljanje podacima), Ujedinjeno upravljanje podacima, gdje su svi korisnički podaci, datoteke konfiguracije mrežne usluge, Pohranjuju se pravila o mrežnom pristupu i ostale informacije. Na primjer, Kad se korisnik u početku poveže s mrežom, Podaci o korisniku provjeravaju se putem podataka u UDM -u.
Urllc (Ultra pouzdana komunikacija s niskim kašnjenjem), Ultra pouzdane i ultra-latencije komunikacije, jedan od tri glavna scenarija od 5G, Cilj je podržati usluge koje su vrlo osjetljive na odgodu i stabilnost, i može biti zajamčena tehnologijom rezanja mreže.
UPF (Funkcija korisničke ravnine), the user plane function, is responsible for forwarding traffic between the wireless access network and Internet/DN, reporting traffic usage, QoS policy implementation, itd., corresponding to the user plane of S/PGW in 4G EPC.
V2X (Vehicle-to-everything), the Internet of Vehicles, aims to connect cars to the Internet, and to connect cars to cars, cars to people, cars and road infrastructure to realize the exchange of information between cars and the outside world, including Connectivity between V2N (vehicle and network/cloud), V2V (vehicle and vehicle), V2I (vehicle and road infrastructure), and V2P (vehicle and pedestrian).